What is Evolution?
The word evolution is used in science to describe change through time. We can speak of the evolution of the Earth, evolution of a molten magma, or evolution of a solar system. Biological evolution refers to how life has changed through time.
Online resources:
What is Biological Evolution?
Simply stated, biological evolution proposes that through the process of natural selection and other natural processes acting over many generations, living things diversify, branching from one species into many. Natural selection acts on genetic variation in a population, such that those best adapted to current conditions have a better chance of surviving to reproduce and thus pass on a favorable trait to succeeding generations. Changes in the genetic composition can also occur without the push of natural selection, especially in small, isolated populations, in which a more or less neutral mutation can spread by chance. Either way, genetic variation can accumulate in a population to the point that it can no longer interbreed with its parent population, and a new species is born. Recent work on 'epigenetics' is looking at evidence that environmental conditions can affect the expression of genetic content of an organism, and that such changes can be passed on, to not only the next generation, but subsequent ones as well.
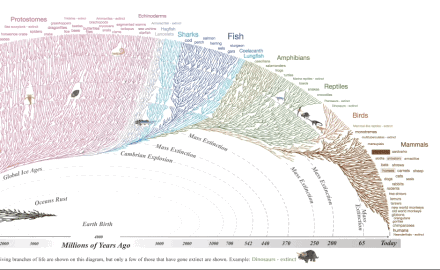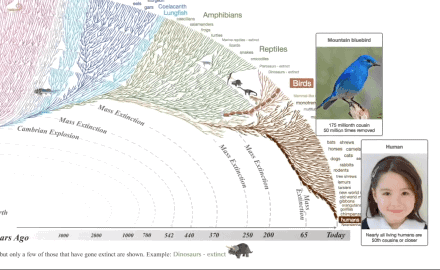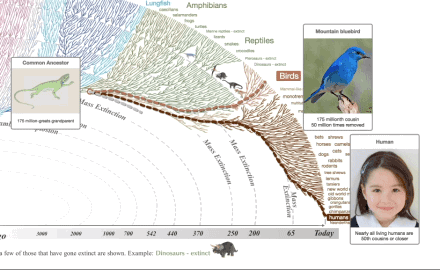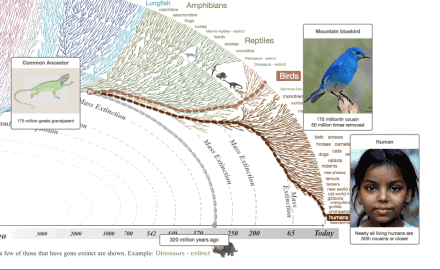
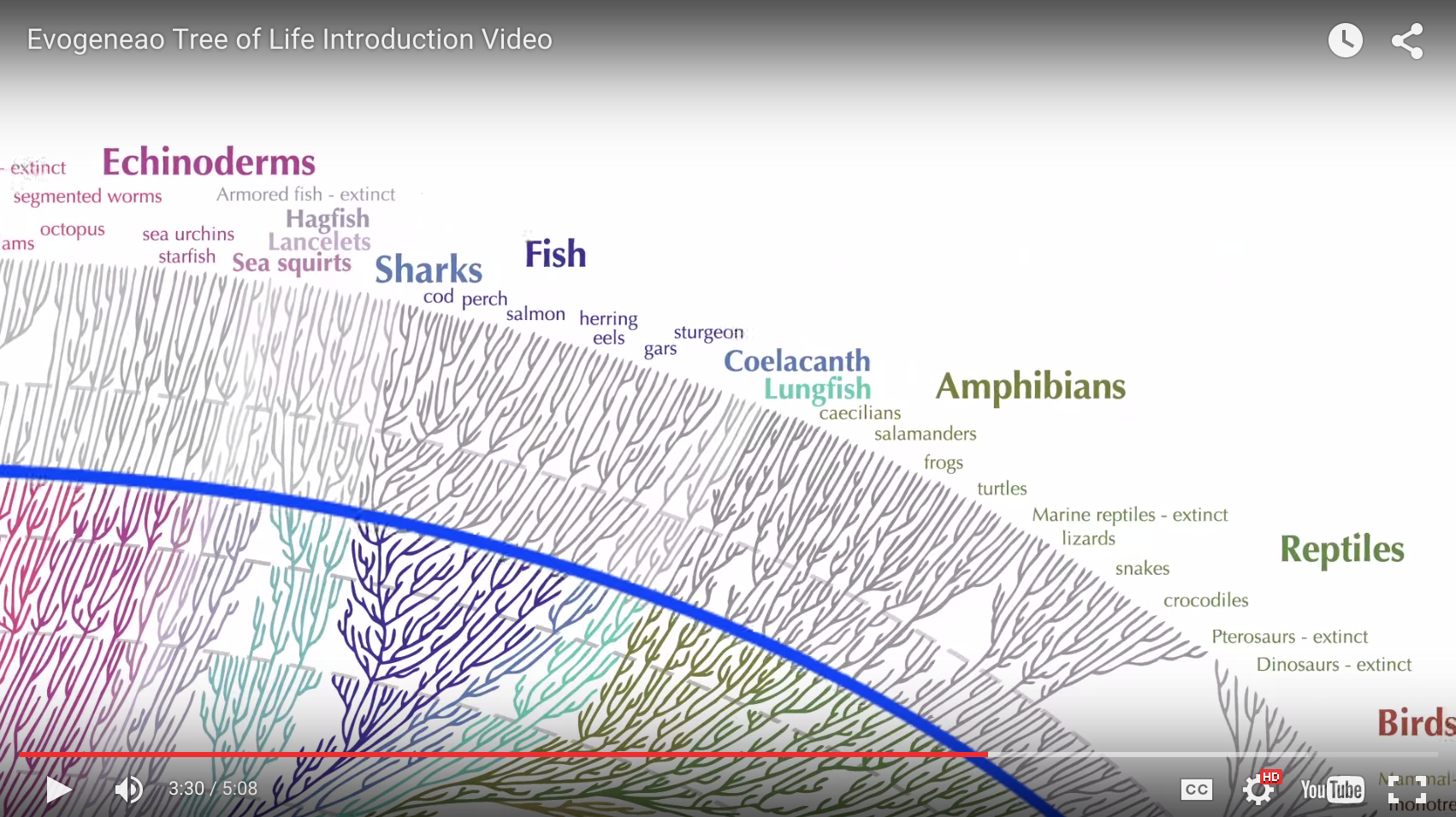
What all this means is that all living things are related to one another through common ancestry with earlier, different life forms. In other words, if you follow your family tree far enough back in time, you will find a common ancestor not only with every other living thing, but also with every thing that ever lived.

We are related not only to every living thing, but to every thing that has ever lived!
Life has changed through time. Life is One Big Extended Family, all related by descent from common ancestors. These statements are as fundamental to scientific understanding of our world as the fact that the earth is a sphere (an oblate spheroid to be precise), is billions of years old, and orbits the sun. Only slightly less sure is the exact mechanism by which life has changed through time. We certainly know that natural selection, lateral gene transfer, genetic drift and other natural processes, including perhaps epigenetics, act to produce this result, but details of the processes involved, and the relative contribution of each one, are an active topic of debate within science. Opponents of evolution use these debates to portray biological evolution as 'a theory in crisis' or just one of several equally plausible models. Nothing could be further from the truth. To accept the opponent's view would be equal to thinking that because scientists debate details of gravitational theory, or quantum theory, or chemical bond theory, that these are 'theories in crisis'! The evidence is clear: Biological evolution is one of the best documented and strongly supported theories in science.

Biological evolution is one of the best documented and most strongly supported theories in science.
Biological Evolution Background
In 1858, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace independently proposed a theory of biological evolution to explain the diversity of life on Earth. Since then the fossil record, DNA studies and other evidence have added, and continue to add, overwhelming support for this view of life's history.
In science, the strength of any theory rests in large part on its ability to make testable predictions and to see those tests confirm the predictions. Darwin's work made several bold predictions that have been spectacularly confirmed since On the Origin of Species was published in November 1859.
View the full set of plate tectonic maps and ancient animal tiles at Briscoe Geology Park in Ashland, Oregon.
First, in Darwin's time the fossil record was just starting to be investigated. One significant observation of the time was that sedimentary rocks beneath (older than) the Cambrian layer appeared to be without fossils. In sedimentary rocks above (younger than) the Cambrian boundary, many different life forms left numerous fossils, which changed gradually, or sometimes abruptly, in younger and younger rocks. If Darwin's theory was correct, fossils of simpler life forms than those in the Cambrian should be present in pre-Cambrian rocks. The fact that at the time they were not known was a problem Darwin acknowledged, but he predicted such fossils would be found eventually. In the last half century at several sites around the world paleontologists have found exactly the sort of simple Pre-Cambrian fossils Darwin predicted.
A second Darwin prediction was that ancient fossils transitional between more recent types would be found. In 1859 there weren't any known, but only a few years later,
Third, in Darwin's time science had no idea how characteristics of living things were passed from one generation to another. But the theory of evolution predicted that a biological mechanism existed which 1) accounted for mutations, 2) explained how they affected bodily form, and 3) recorded the history of genetic changes through time. Just such a mechanism was discovered in the 1950's in the DNA molecule. Since then everything we have learned about DNA and genetics supports the theory of biological evolution. It is perhaps its most spectacular and strongest confirmation. See: ghr.nlm.nih.gov/handbook/basics/dna
Fourth, Darwin reasoned that because chimpanzees, the apparent closest relatives of humans, lived in Africa, fossils of creatures transitional between humans and apes would be found in Africa, and that the older the fossils the more ape-like they would appear. Starting in the 1920's and continuing through very recent discoveries, this prediction has been spectacularly confirmed. The American Museum of Natural History has a fantastic exhibition on human evolution.
To be scientific, any theory must be falsifiable. There are many ways that biological evolution could be proved false. One example would be if Homo sapiens fossils were to be incontrovertibly found in any rocks older than a few hundred thousand years. But even after 150 years, no solid evidence has ever been found that would prove evolution false. In fact, all observations have supported evolutionary theory. The idea of intelligent design on the other hand, although touted as an alternative to evolution, is in fact not a scientific theory because it cannot be falsified. Worse, if intelligent design were taught on an equal footing with evolution, alchemy could be taught alongside chemistry, and astrology alongside astronomy. An intelligent design proponent admitted this absurdity under oath during the famous Kitzmiller trial.
See: Intelligent Design on Trial
There is no better way to celebrate the wonder of evolution and the family of life on Earth, than to use Darwin's own words…

To find out more about evolution and science, please visit these interesting websites: